RWTH Aachen Campus is an association of various research institutions of the RWTH Aachen University and numerous renowned industrial companies. It was founded in 2008 as RWTH Aachen Campus GmbH. It was established in the style of large-scale university campus often found in America. There, the strength and force of individual actors are bundled through local proximity and active cooperation.
RWTH Aachen Campus GmbH is a subsidiary of RWTH Aachen University and the City of Aachen. As such, it is responsible for the planning, implementation and controlling of the overall campus concept. It has the overall purpose of researching economically and socially relevant problems and research topics in an interdisciplinary approach. RWTH Aachen Campus consists of topic-oriented clusters (currently six): Smart Logistics Cluster, Heavy-Duty Drives Cluster, Photonics Cluster, Bio-Medical Engineering Cluster, Production Engineering Cluster and Sustainable Energy Cluster. The individual clusters are divided into centers. They form the operative units in which relevant future issues are examined, researched and processed with visionary and innovative ideas and approaches. For more information click here.
The term Cluster Smart Logistics stands for a network of stakeholders and research entities, whose work is dedicated to the subject of smart logistics. The cluster is part of a network of other clusters on the RWTH Aachen Campus (a total of 16 different clusters is currently being set up, as of 2018). Six centers and two institutions, each researching a specific, relevant issue with a visionary approach, are currently assigned to this particular Cluster Smart Logistics. In addition to the Service Performance Center, these include the Center Enterprise Resource Planning, the Center Connected Industry, the Center Smart Commercial Building, the European 4.0 Transformation Center, the Industry 4.0 Maturity Center, the Demonstration Factory and the Electro Mobility Laboratory. Further information on the Cluster Smart Logistics can be found in the official brochure, which you can view and download here free of charge.
Here at the Service Performance Center, we work with industry and research Partners to provide strategic consulting services. We collaborate with companies primarily in the framework of consortium projects, studies, and benchmarking. The focus is on the development of new smart services, the identification of digitalization potentials and strategies or the identification of best practices in the context of consortial benchmarking.
Companies can become active members of the Service Performance Center by officially enrolling. Thus, they benefit from the Center’s full range of services through long-term collaboration. An overview of the available options can be found here. In addition, the Service Performance Center of course also cooperates with non-enrolled companies. Interested in specific Smart Service related topics and digital business models? Get in touch with us! We are happy to make you an individual offer.
Further education offers, which are another field of activity of the Service Performance Center, are accessible to members of the Center Smart Service Community as well as to all other interested companies. An example of one of our training courses is the certificate Course “Smart Service Manager”, which we are happy to be offering again in 2019 and 2020 because the course was such a great success last in 2018.
Consortial projects at the Service Performance Center are industry-related, highly practice-focused projects with specific focus areas, such as the development and implementation of digital services and digital business models. These projects are always carried out by consortia consisting of industrial partners. They work together on a topic that is of particular relevance to all of them. The close side-by-side work of leading companies is the special strength of consortial projects, as this procedure bundles forces and creates synergy effects.
All projects initiated by the Service Performance Center are Independent and strongly focused on practice related topic, which results in the fast development of ready-to-use solutions. The solutions are made available exclusively to the project participants. Typical project results include target-oriented roadmaps and demand-oriented solutions for a particular challenge. Many projects focus on the analysis, identification and structuring of digitalization potentials for various company areas. An overview of our current projects, studies and benchmarkings can be found here.
The Service Performance Centercarries out consortial studies, a specific type of consortial project. Consortial studies usually follow clearly defined process steps to answer a previously defined research qestion. Just like consortial projects, consortial studies are led by a consortium of industry partners. They work together on a joint study goal. The studies help to collect valuable data and insights which are relevant for the strategy and business development of the companies involved. Furthermore, the results are also used for the development of a new smart services.
A consortial benchmarking is a specific type of a consortial study. Its aim is to identify companies, who are particularly successful in a specific work field or method. Why are they more successful than others? A consortial benchmarking wants to find answers to this question. At the end of a consortial benchmarking, the most succesful companies are awared the title of “best practice company” – usually, the five best are chosen. Again, consortial benchmarkings are also carried out by a consortium consisting of cooperating industry companies.
A consortial benchmarking follows a strict pattern, used to identify the succesful companies and their used Methods. First, the benchmarking topic is defined and the companies for the consortium are selected. Afterwards, a questionnaire is designed and used as part of the companies` analyses to detect their most promising methods and strategies. For this, participants are acquired all over Europe and asked to fill out the questionnaire. Based on the collected data, it is analysed which companies could – potentially – carry the title “best practice”. Then, the chosen candidates are interviewed in in-depth telephone interviews and presented with anonymous use cases. All this content is incorporated into the final selection of successful practices. Once they receive their Award, they hold a special competitive position on the market with the official award as such.
The consortium partner benefit from the scientific overview of the success principles of the analysed companies. Furthermore, they profit from an exclusive insight into the companies` everyday practice. As a result, market transparecy over which companies are successful in a specific industry area and why is increased significantly.
One example of an already completed consortial benchmarking is the one on “Data-based Services”, which was carried out in 2016. It researched the strategies used by succesful companies for the development and implementation of smart services. The latest Service Performance Center benchmarking is on the topic of “Subscription Business”. It analyses how subscription business models can be turned into reality. Furthermore, it researches the additional benefit of subscription businesses for customers and companies. More Information here.
The term stands for services that are based on digitally available data. This was collected and analysed in advance by a comptuer or machine. This data (such as production data) provides the potential to create numerous new kinds of services such as Smart Services (see below). These, in return, can lead to the creation of new Business models and create new opportunities for monetization. Collected production data, e.g., provides information on the wear and tear, workload and defects of a production line. Based on this information, maintenance planning can be improved and production line downtime reduced.
A smart service is a service that aggregates and processes usage- or context-related data. The data generates from digitally connected physical objects (so-called smart products). The aim of the smart service is to create an added value. This can be in the form of intelligent control options or the adaptation and optimisation of functions. The added value created by smart services can also be noticeable elsewhere, for example only on side of the actual service user.
The smart product is a neccessary prerequisite for the smart service. It can be used by each of the partner involved in the value-added-chain. However, it also combines their competencies and recources, activities and service results. As a result, it creates a cooperative service performance. The data sent by the smart product is collected by a software solution and analysed. Then, it triggers an action based on that data or allows to make action-based decisions. This is the actual smart service. Actions or process steps that would normally be carried out by operators are handed over to the combination of smart product, software solution and data analysis procedures. In the long-run, this simplifies and accelerates processes and activities.
A business model scenario shows how a theoretical business model can be combined with the technology solutions that are required for ist realisation. Example: A machine manufacturer makes a special machine available to a manufacturer as a pay-per-hour option. In addition to the business model and the associated framework conditions, the type of use of these machines and their condition must be known at all times. To achieve this, the following technology components are required: Sensors (for recording machine data), Edge Computing (for calculating relevant information) and Connectivity (for sending the information to the machine manufacturer).
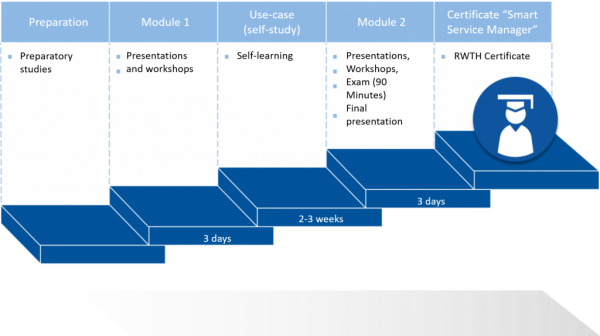
Courses certified by the RWTH Aachen University such as the “Smart Service Manager” are further education courses that are part of a certified education program of the RWTH Aachen University. The courses include two modules over the course of three days each as well as one self-responsible learning phase, during which the participants work on a case alone. The course consists of speeches and presentations given by experts from various industry and research sectors. They highlight current trends and developments in the management of data-based services. The portfolio also includes interesting use-cases as well as practical exercises.
Participants of the RWTH-certified course “Smart Service Manager” will be taught key skills that are required for the successful development and management of data-based services. The course lasts six days in total (2×3 days), the target group consists of CEOs and managers. Between the two parts of the course, participants will be asked to work on business cases alone in a self-study phase. More information about the course content and registration options can be found here!